Futuros
Opera o haz coberturas sin comisiones de swap
Hacer trading es riesgoso
ÍNDICES DE
US, REINO UNIDO, UE Y ASIA
TRADING DESDE
$0 COMISIÓN
HASTA
1: APALANCAMIENTO 100
4 FUTUROS
ÍNDICES DE
US, REINO UNIDO, UE Y ASIA
TRADING DESDE
$0 COMISIÓN
HASTA
1: APALANCAMIENTO 100
4 FUTUROS
Opera en mercados de futuros
Símbolo
Oferta
Preguntar
Spread

*Los precios de esta página son orientativos. Los precios de los instrumentos con menor liquidez, como, entre otros, pares de divisas, acciones e índices exóticos, no se actualizan con tanta frecuencia como los instrumentos negociados habitualmente. Consulte dentro de su plataforma MT4/MT5 para conocer los últimos precios en vivo
¿Qué son los futuros?
Los futuros son instrumentos derivados que obligan a las partes involucradas a comprar o vender un activo en una fecha futura predeterminada y a un precio establecido (determinado por el activo subyacente). La naturaleza de estos contratos los hace ideales tanto para el trading como para las coberturas. Los contratos de futuros tienen una fecha de vencimiento y no implican comisiones de swap, por lo que son muy usados para operaciones a largo plazo.

Sin swaps nocturnos

Perfectos para coberturas

Opera con apalancamiento
¿Cómo funciona el trading de futuros?
El trading de futuros funciona de manera similar al trading de CFDs. Sin embargo, cada contrato de futuros tiene una fecha de vencimiento. Puedes cerrar tu posición en cualquier momento o dejar que el contrato alcance su vencimiento. Si deseas mantener tu posición después de la fecha de vencimiento, puedes abrir una nueva posición en un contrato de futuros con una fecha de vencimiento posterior. Los contratos de futuros se actualizan frecuentemente con nuevas fechas de vencimiento. Además, el vencimiento de cada contrato se indica con el sufijo del símbolo. Por ejemplo, «DJ.H24» es un contrato de futuros del Dow Jones que vence en marzo de 2024. Por otro lado, «SP.N24» es un contrato de futuros del S&P 500 que vence en julio de 2024.
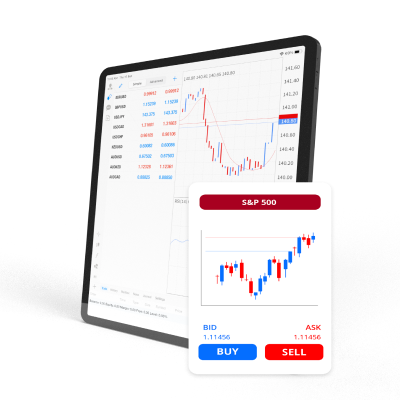
Precios de compra y venta (bid y ask)
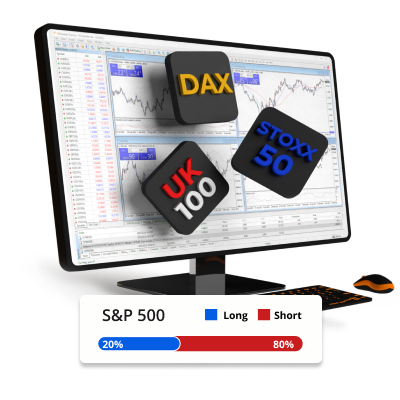
Entra largo o corto
Los futuros se negocian en lotes

En el trading de futuros se usa apalancamiento y margen
Ejemplo de trading de futuros
Decides comprar 0.1 lotes de futuros del S&P 500, que tiene un valor de mercado de 4500, utilizando un apalancamiento de 100:1.

5 contratos de futuros x 4500 = $22 250
USD 22,250
USD 22,250 / 100 = USD 225
Ahora tienes una posición en largo en el S&P 500 por un valor de $22 250. Como los futuros se negocian con apalancamiento, solo se utilizan $225 de tu cuenta de trading como margen. Después de algún tiempo, el precio del S&P 500 se mueve y decides vender.
Escenario 1

El S&P 500 sube de 4500 a 4600 y decides vender.
Así es como se calcula la pérdida o ganancia de la operación:
P/G = (Precio actual - Precio inicial) x Valor de la posición) / Precio actual
P/G = ((4600 - 4500) × 22,250) / 4,600
P/G = (100 × 22,250) / 4,600
P/G= 483.70
Escenario 2

El S&P 500 baja de 4500 a 4400 y decides vender.
Así es como se calcula la pérdida o ganancia de la operación:
P/G = (Precio actual - Precio inicial) x Valor de la posición) / Precio actual
P/G = ((4400 - 4500) × 22,250) / 4,400
P/G = (-100 × 22,250) / 4,600
P/G = -483.70
Por qué TIOmarkets
Por esto personas como tú eligen TIOmarkets

Spreads desde 0.0 pips
Opera con spreads variables sin alterar en nuestra cuenta Raw

Trading sin comisiones
Opera desde $0 por lote en nuestras cuentas VIP Black o Standard

MT4 Y MT5
Plataformas de trading avanzadas para escritorio, web y celulares

Ejecución rápida de órdenes
Procesamiento de órdenes eficiente y confiable en milisegundos

Leverage ilimitado.
Opera con un apalancamiento hasta ilimitado en la cuenta Standard

Bono de lealtad del 30%
Obtén un bono en cada depósito a nuestra cuenta Standard
Opera en las plataformas de trading MT4 o MT5
Desde tu escritorio, navegador de internet o móvil
Empieza a hacer trading en minutos
Así es como funciona

PASO 1
Registrarse
Completa tu perfil y crea tu cuenta, solo toma unos minutos

PASO 2
Verificar
Carga tu comprobante de identidad y domicilio, esto es obligatorio antes de retirar

PASO 3
Depositar fondos
Elige entre nuestros cómodos métodos locales e internacionales y deposita al instante
PASO 4
Operar
Descarga la plataforma, transfiere fondos a tu cuenta, inicia sesión y comienza a operar
Hacer trading es riesgoso