Giao dịch tương lai
Giao dịch hoặc phòng ngừa rủi ro mà không có phí hoán đổi
Giao dịch tiềm ẩn rủi ro
CHỈ SỐ TỪ
US, ANH, EU VÀ CHẨU Á
GIAO DỊCH TỪ
$0 ỦY NHIỆM
ĐẾN
1: ĐÒN BẨY 100X
4 TUỔNG LAI
CHỈ SỐ TỪ
US, ANH, EU VÀ CHẨU Á
GIAO DỊCH TỪ
$0 ỦY NHIỆM
ĐẾN
1: ĐÒN BẨY 100X
4 TUỔNG LAI
Giao dịch thị trường tương lai
Biểu tượng
Đấu thầu
Hỏi
Chênh lệch giá

*Giá trên trang này là chỉ định. Giá của các công cụ có tính thanh khoản thấp hơn, chẳng hạn như nhưng không giới hạn đối với các cặp tiền tệ kỳ lạ, cổ phiếu và chỉ số không được làm mới thường xuyên như các công cụ được giao dịch phổ biến. Vui lòng kiểm tra bên trong nền tảng MT4/MT5 của bạn để biết giá trực tiếp mới nhất
Hợp đồng tương lai là gì
Hợp đồng tương lai là hợp đồng phái sinh bắt buộc các bên liên quan phải mua hoặc bán một tài sản vào một ngày được xác định trước trong tương lai và ở mức giá ấn định. Giá được tính từ tài sản cơ bản và bản chất của các hợp đồng này khiến chúng hữu ích cho việc giao dịch và phòng ngừa rủi ro. Hợp đồng tương lai có ngày hết hạn và không có phí hoán đổi qua đêm, vì vậy chúng rất hiệu quả về mặt chi phí cho giao dịch dài hạn.

Không có giao dịch hoán đổi qua đêm

Tuyệt vời cho việc phòng ngừa rủi ro

Giao dịch với đòn bẩy
Giao dịch tương lai hoạt động như thế nào
Giao dịch tương lai hoạt động tương tự như giao dịch CFD, nhưng mỗi hợp đồng tương lai đều có ngày hết hạn. Bạn có thể đóng vị thế của mình bất cứ lúc nào hoặc bạn có thể để hợp đồng đóng khi hết hạn. Nếu bạn muốn duy trì vị thế của mình sau ngày hết hạn, bạn có thể mở một vị thế mới trong hợp đồng tương lai có ngày hết hạn muộn hơn. Hợp đồng tương lai được cập nhật thường xuyên với ngày hết hạn mới và ngày hết hạn của mỗi hợp đồng tương lai được biểu thị bằng hậu tố ký hiệu. Ví dụ: DJ.H24 là hợp đồng tương lai Dow Jones hết hạn vào tháng 3 năm 2024. SP.N24 là hợp đồng tương lai S&P 500 hết hạn vào tháng 7 năm 2024.
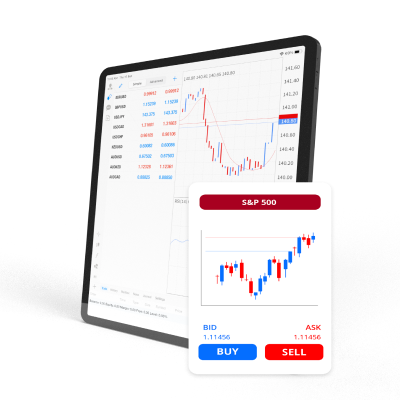
Đặt giá thầu và yêu cầu giá
Mua vào hoặc bán ra
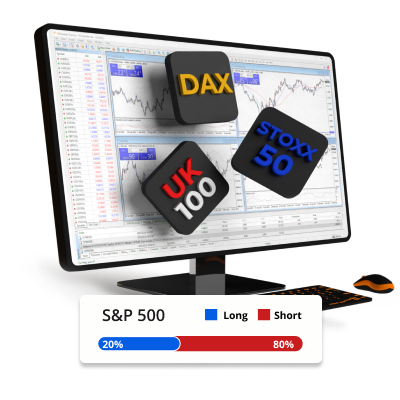
Hợp đồng tương lai được giao dịch theo lô

Giao dịch tương lai liên quan đến đòn bẩy và ký quỹ
Ví dụ về giao dịch tương lai
Bạn quyết định mua 0,1 lô hợp đồng tương lai S&P500 với giá 4500 sử dụng đòn bẩy 100:1.

5 hợp đồng tương lai x 4500 = 22.250 USD
USD 22,250
USD 22,250 / 100 = USD 225
Bây giờ bạn đã mở một vị thế mua S&P500 trị giá 22.250 USD. Vì hợp đồng tương lai được giao dịch bằng đòn bẩy nên chỉ có 225 USD được sử dụng làm tiền ký quỹ từ tài khoản giao dịch của bạn. Sau một thời gian, giá của S&P500 di chuyển và bạn quyết định bán.
Kịch bản 1

S&P500 tăng từ 4500 lên 4600 và bạn quyết định bán.
Đây là cách tính lãi hoặc lỗ trong giao dịch.
P/L = (Giá hiện tại - Giá ban đầu) x Giá trị vị thế / Giá hiện tại
P/L = ((4600 - 4500) × 22,250) / 4,600
P/L = (100 × 22,250) / 4,600
P/L= 483.70
Kịch bản 2

S&P500 giảm từ 4500 xuống 4400 và bạn quyết định bán.
Đây là cách tính lãi hoặc lỗ trong giao dịch.
P/L = (Giá hiện tại - Giá ban đầu) x Giá trị vị thế / Giá hiện tại
P/L = ((4400 - 4500) × 22,250) / 4,400
P/L = (-100 × 22,250) / 4,600
P/L = -483.70
Tại sao nên chọn TIOmarkets
Đây là lý do tại sao những người như bạn chọn TIOmarkets

Spreads từ 0.0 pips
Giao dịch với chênh lệch biến đổi thô trên tài khoản Raw của chúng tôi

Giao dịch miễn phí hoa hồng
Giao dịch từ $0 mỗi lot trên tài khoản VIP Black hoặc Standard của chúng tôi

MT4 & MT5
Nền tảng giao dịch tiên tiến cho máy tính để bàn, web và thiết bị di động

Khớp lệnh nhanh
Xử lý lệnh hiệu quả và đáng tin cậy trong vài mili giây

Đòn bẩy leverage không giới hạn.
Giao dịch với đòn bẩy không giới hạn trên tài khoản Standard của chúng tôi

Thưởng 30% Loyalty
Nhận thưởng khi nạp tiền vào tài khoản Standard của chúng tôi
Giao dịch trên nền tảng MT4 hoặc MT5
Từ máy tính để bàn, trình duyệt internet hoặc thiết bị di động
Bắt đầu giao dịch chỉ trong vài phút
Cách thức hoạt động như sau

BƯỚC 1
Đăng ký
Hoàn tất hồ sơ và tạo tài khoản của bạn, chỉ mất vài phút

BƯỚC 2
Xác minh
Tải lên giấy tờ xác minh danh tính và địa chỉ, yêu cầu trước khi rút tiền

BƯỚC 3
Nạp tiền
Chọn các phương thức nội địa và quốc tế thuận tiện và nạp tiền ngay lập tức
BƯỚC 4
Giao dịch
Tải nền tảng, chuyển tiền vào tài khoản, đăng nhập và bắt đầu giao dịch
Giao dịch tiềm ẩn rủi ro